| doc/png | ||
| elf2uf2 | ||
| generated/pico_base/pico | ||
| lib | ||
| msc_content | ||
| pico-sdk | ||
| src | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| cmake_install.cmake | ||
| CMakeDoxyfile.in | ||
| CMakeDoxygenDefaults.cmake | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| pico_sdk_import.cmake | ||
| README.md | ||
Motenpoche
Motenpoche ([mot-ɑ̃-pɔʃ] - like in "Mot en poche", French for "word in [your] pocket") is a physical password vault to carry around your secrets securely. Once connected to a PC and unlocked with a main passphrase it will paste passwords selected from your collection by pressing a button.
Passwords can be provisioned with the help of a host-side command line tool that can be run on a GNU/Linux PC, either one by one or importing from an existing (software) vault.
Status
This project is still in an early alpha phase and has not been properly tested yet.
There are in particular, the following known security issues:
- No proper string boundary check
- No proper serial protocol hardening
- Incomplete password wiping from memory after use
Use at your own risk, no guarantee provided on loss of secret data, service profiles, bank details or other relevant information that have been stored on the device. The author and the contributors recommend not to use this software for any purpose other than security auditing, research and study, and they cannot be held responsible or any damage of any kind resulting from any proper or improper use.
Software License
The software distributed in this project is uniquely released under the terms of GNU GPL v.2.
What is this for
I'm lazy and skeptical when it comes to distributed password managers. I don't like the idea of keeping a wallet of passwords on a cloud server. On the other hand, I'm oftern traveling and carrying a laptop, where I must periodically update my password database if I want to access services when I'm abroad.
This system was created to have a temporary physical storage that can be carried around (and lost, or forgotten on a public transportation...) with reduced risk.
More features may be available in the future based on user experience.
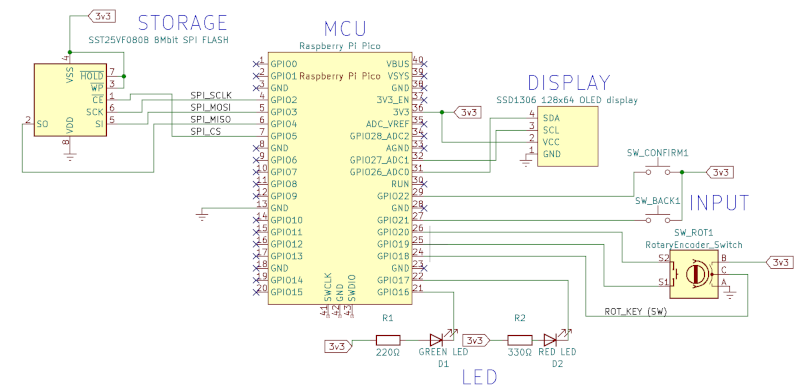
Hardware design
The design is based on the rp2040 "Raspberry Pi Pico" board, with a few components and peripherals connected as shown here:
Pinout
Here is a recap of the pins used on the Raspberry PI, as configured by the software in this repository:
| Pin | Function | Connects to | Pullup/pulldown |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO2 | FUNC_SPI | SPI Flash SCLK | none |
| GPIO3 | FUNC_SPI | SPI Flash MOSI | none |
| GPIO4 | FUNC_SPI | SPI Flash MISO | none |
| GPIO5 | OUT | SPI Flash CS | none |
| GPIO16 | OUT | Green LED cathode | none |
| GPIO17 | OUT | Red LED cathode | none |
| GPIO18 | IN | Rotary Keypress | pull-up |
| GPIO19 | IN | Rotary S1 | pull-down |
| GPIO20 | IN | Rotary S2 | pull-down |
| GPIO21 | IN | Pushbutton "Back" | pull-down |
| GPIO22 | IN | Pushbutton "Confirm" | pull-down |
| GPIO26 | FUNC_I2C | I2C Display SDA | none (automatic pull-up) |
| GPIO27 | FUNC_I2C | I2C Display SCL | none (automatic pull-up) |
How it works
The simple idea behind it is that the device does not carry any secret in plain text. The passwords are stored on an external SPI flash, encrypted and signed with unique keys created when the device is initialized. The encryption key is symmetrical (ChaCha) and can be derived on board using the main passphrase, which is entered through the rotary and the confirm button.
The signature key (ECC256) is created during device initialization on the PC that holds it. The key is then used to sign the passwords to be added to the vault.
Passwords can be provisioned using the host tool, either one by one, or importing from a CSV file previously exported from, e.g. a software password manager or a web browser.
When the device is unlocked, selecting the service needed from the "Services" menu will paste the password onto the PC. The user should ensureto select the right password box before activating the service on the device to prevent password leaks in clear text on the PC screen.
Multiple paste modes are available from the "Settings" menu onboard. The device can for example fill username + password web forms automatically, by typing in the username, then the TAB key, then the password and finally ENTER.
Initialization
The device can be initialized using a TOFU (Trust on First Use) mechanism. When
the device is in "factory mode", it can be initialized using the host command line
application, selecting the "TOFU" function. The application will then ask to input
(and confirm) the main password that will be used to unlock the device.
As mentioned, this procedure also creates the main signature key to provision
passwords. If you want to be able to add passwords to the vault from different
PCs, ensure that you carry a copy of the key generated in ~/.pvault/.
Adding password services
Passwords can be provisioned using the host tool, either manually or importing them from a CSV file. The information is then encrypted on the PC using the main password, signed using the signature key and transmitted to the device.
The device must be unlocked in order to receive password services to add to the database. Uploading a single password may take a few seconds because the device verifies that the source of the information is trusted.
What does the PC see?
When you connect motenpoche to your PC, it will show up as three different devices:
-
A USB drive, containing the source and the binary of the host command line tool
mep[TODO] -
A serial port (typically /dev/ttyACM0), used by the host command line tool to communicate with the device, initialize it after factory reset and upload passwords.
-
A HID keyboard device. Motenpoche will use a 'fake' keyboard to input the selected password when requested.
Security considerations
-
The algorithm used to generate the encryption key is PBKDF2, using SHA512 for hashing, and a random salt generated when the device is initialized
-
Neither the passwords, nor the main secret, or any private key is ever stored on the device. When the device is turned off, the storage is encrypted.
-
Password checking is performed on board by decrypting the signature stored in the initial settings page, and then checking for the integrity (sha) and authenticity (ecc signature) of the page itself. Each password is then decrypted on demand and sent to the PC through the HID keyboard device.
-
Passwords can still be intercepted by a keylogger, e.g. using a USB sniffer. (This is not very different from an actual USB keyboard).
-
Main keys and passwords are never transmitted via USB.
Future development
-
The command line tool
mepmight have a function to "rekey" the device, changing the salt and the constant part of the IV used for the encryption -
Store private keys / custom secret files in the storage device. Those would be invisible until the device is unlocked.
Compiling and flashing to Raspberry-pi pico:
To compile the firmware run the following from the source directory:
mkdir build
cd build
make -C ../msc_content
cmake .. -DFAMILY=rp2040 -DPICO_SDK_PATH=/path/to/motenpoche/pico-sdk
Host tool
A copy of the host tool mep is in the msc_content directory. Compile using
"make", then run the tool pointing it to the correct USB serial device, e.g.:
./mep /dev/ttyACM0